This is a great time for functional medicine. There’s so much research emerging on how the different systems in your body are connected, lending even more proof that the whole-body functional medicine approach to health is truly the best option.
One of the most exciting developments has been on understanding how natural substances mimic and interact with the chemicals and systems in our bodies. Recent focus has been on the plant extract CBD or cannabidiol. Yet there’s actually something besides cannabinoids already in your body that works in much the same way.
That’s why I included palmitoylethanolamide, or PEA for short, in my ZenAdapt™ supplement. It lends the benefits — and more! — of CBD without the worry about side effects or even legality.
I’ll explain the similarities and differences between CBD and PEA, starting with the system in your body that works with them.
What Is the Endocannabinoid System?
There’s an entire SYSTEM in your body that was only just discovered in the 1990s. Of course, it’s been there all along, yet we’ve only recently had the tools to recognize it. And we’ve just scratched the surface on how it works.
What we do know is that it’s a three-part system of chemicals called endocannabinoids including anandamide, receptors in your nervous system that bond with them, and enzymes that break them down. This system is literally a bridge between body and mind. In short, its job is to maintain homeostasis, or balance, in your body. I’ll circle back to that idea later.
The system has a role in chronic diseases and immune function
There’s ongoing research into how the system works in such processes as reducing inflammation. Both CBD and PEA interact with this system. You can learn more about the endocannabinoid system in this article.
What Is CBD?
CBD is one of more than 100 compounds called cannabinoids that are similar to the endocannabinoids your body makes. Cannabinoids naturally occur in Cannabis sativa plants. That’s the marijuana plant and also the hemp plant. The two look identical and the only difference between them is the amount of another cannabinoid called tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC, they each contain. THC is the compound in marijuana that results in a “high.”
What are the Benefits of CBD?
Some people who take CBD feel the effects right away, while others experience nothing at all. Its proponents believe CBD:
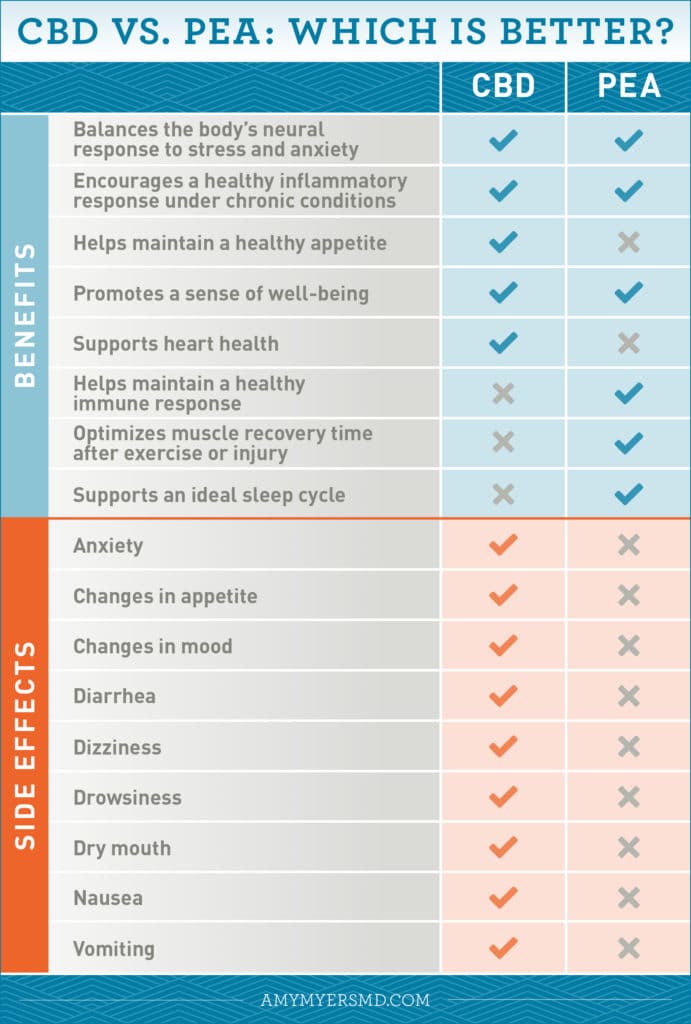
- Balances the body’s neural response to stress and anxiety
- Encourages a healthy inflammatory response under chronic conditions
- Helps maintain a healthy immune response
- Helps maintain a healthy appetite
- Promotes a sense of well-being
- Supports heart health
What Are the Side Effects of CBD?
While it’s generally deemed safe it does have side effects. These can include:
- Anxiety
- Changes in appetite
- Changes in mood
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Vomiting
What Is the Best Source of CBD?
That’s one of the big issues with CBD. Hemp is legally grown and sold throughout the U.S. If CBD is extracted from the stems and leaves of marijuana, it may contain THC and may or may not be legal where you live. If it’s extracted from the stems and leaves of hemp, it still may or may not meet federal guidelines.
THC, the main difference between hemp and marijuana, is present in large amounts in the marijuana plant and in negligible amounts in the hemp plant. At the moment, marijuana is illegal at the federal level, although it is legal to varying degrees in many states.
That’s one of the big issues with CBD. Hemp is legally grown and sold throughout the U.S. If CBD is extracted from the stems and leaves of marijuana, it may contain THC and may or may not be legal where you live. If it’s extracted from the stems and leaves of hemp, it still may or may not meet federal guidelines. Oils extracted from the seeds of either plant don’t contain CBD, so hemp seeds and hemp seed oil are not a source of CBD.
What Is the Typical Dose of CBD?
Only one medication with CBD, Epidiolex®, has been approved for use by the FDA.1 Epidolex® is a compound that contains an extremely high dose of CBD, 100 mg of CBD twice daily. It has been used with great success on a type of childhood epilepsy called Dravet syndrome,2 for which there is no other effective treatment.
Once the FDA approved that first medication, a “wild west” of companies began producing and distributing a wide variety of CBD products in oils, lozenges, creams, gummies, and even water. However, even though these products generally have far less than of the FDA-approved dosage, they’re still very expensive.
The FDA has no guidelines for dosing for any product other than Epidiolex®. However, many people involved in the industry recommend 1-6 mg per 10 pounds of body weight. Products can range from anywhere from 6 mg to 60 mg of CBD per mL of product. Yet, according to a recent sampling, only 30% of products actually contain the amount of CBD claimed on their label,3 so it’s difficult to determine an exact dosage.
Because of the lack of labeling, the uncertainty about the appropriate dosage, and the potential for products to include some levels of THC, I don’t generally recommend CBD.
 Dr. Amy Myers
June 7th, 2020
https://content.amymyersmd.com/article/best-cbd-supplement/CBD Vs. PEA, Which is Better? – Infographic – Amy Myers MD®
Dr. Amy Myers
June 7th, 2020
https://content.amymyersmd.com/article/best-cbd-supplement/CBD Vs. PEA, Which is Better? – Infographic – Amy Myers MD®What Is Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA)?
Unlike CBD, palmitoylethanolamide already exists in your body. Like the endocannabinoid anandamide that your body naturally produces, it’s a fatty acid amine. It interacts with inflammatory cells in the nervous system.4 It’s broken down in your body by an enzyme called fatty acid amide hydrolase, or FAAH.
PEA blocks the expression of the FAAH gene. This serves to boost the activity of your natural cannabinoids because they aren’t broken down and more of them can circulate.
FAAH also breaks down the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2. PEA helps protect these receptors from FAAH, which results in more sensors that can respond positively to stimulation. In short, more PEA means less FAAH.
PEA can also modulate sensitized TRPV1 receptors, supporting the body’s healthy response to inflammation and pain.5 It also activates a protein called PPAR-alpha. This protein plays a role in a large array of functions from supporting your body’s energy levels and fat-burning processes to optimizing your body’s response to inflammation.
Do you remember I mentioned homeostasis, or balance, in the beginning of this article? The research on PEA points to the fact that it doesn’t have just one way of working. Instead, it works synergistically with other elements in your body.6 In fact, it’s something called an endogenous modulator. That means it’s something produced by your body for the purpose of maintaining balance.
What Are the Benefits of PEA?
Generally, PEA needs to build in your body over time to be most effective. Recent research has focused on PEA’s impact on mast cell activation and glial cell behaviors that influence inflammation. In fact, PEA has been shown to:
- Balance the body’s neural response to stress and anxiety
- Encourage a healthy inflammatory response under chronic conditions
- Help maintain a healthy immune response
- Optimize muscle recovery time after exercise or injury
- Promote a sense of well-being
- Support an ideal sleep cycle
What Are the Side Effects of PEA?
Perhaps the most encouraging piece of news about PEA is that it isn’t known to have any negative side effects at all.
What Is the Best Source of PEA?
Though PEA is found in such foods as egg yolks, peanuts, and soy for many people, these foods are highly inflammatory. For that reason, I recommend anyone who wants to take advantage of PEA’s incredible benefit to take the supplemental form.
Supplemental PEA can be synthesized to create the exact molecular structure as what’s already in your body. CBD is similar, yet not an exact match, to your natural endocannabinoids. PEA is also a lot less expensive, and it’s much easier to ensure precise quantities. And remember it has virtually no side effects like CBD does.
What Is the Typical Dose of PEA?
Recent clinical trials in diabetes patients with peripheral neuropathy tested a daily dosage of between 300 mg and 1200 mg. At least one promising approach suggests an initial daily dose of 600 mg to 1200 mg for 3-4 weeks, followed by a maintenance dose of 300 mg to 600 mg may be most effective when PEA is used on its own.
Why I Chose PEA instead of CBD for my ZenAdapt™
As a medical doctor and someone you trust, I could never put ANYTHING in any of my supplements that even hinted at being a controlled substance. Our well-being is just too important to me!
In addition to having its own benefits, it also boosts the effectiveness of other adaptogens in your body.
PEA is well known to have something called the “entourage effect.” That’s why, when I was selecting the adaptogenic herbs to include in my physician-formulated ZenAdapt™, I chose to add 400 mg of PEA per dose to increase the power of:
Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha has been shown to support a calm mind, a healthy inflammatory response, and balanced blood pressure. It’s even been shown to boost the activity of free-radical scavengers.
Rhodiola
Too much cortisol (your primary stress hormone) can deplete your nutrient reserves, impair memory, and have devastating effects on your blood pressure, blood sugar, and metabolism. Rhodiola is an adaptogen that can promote a balanced production of cortisol during stressful situations.
Saffron
The famed “$10,000 spice,” saffron is known for being the most expensive spice in the world. It’s worth every penny! Saffron has well-demonstrated effects on supporting healthy weight loss, sexual function, and free-radical fighting activity in the body.
I formulated my new ZenAdapt™ to support your body and mind when you experience fatigue, overwork, stress, or occasional anxiousness. The effects of the special blend of adaptogenic herbs I included is naturally boosted by PEA so that you can achieve an optimal state of calm and relaxation, even on your most hectic days.

Article Sources
- https://www.epidiolex.com/.
- https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/All-Disorders/Dravet-Syndrome-Information-Page.
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2661569.
- //accurateclinic.com/accurate-education-palmitoylethanolamide-pea/.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5429331/#bph13580-bib-0143.
- https://selfhacked.com/blog/palmitoylethanolamide-pea/.
