Significant science is showing that chemical compounds in Cannabis sativa have beneficial properties. Regardless of how you may feel about the recreational use of marijuana (aka pot or weed), or even medical marijuana, these compounds, called cannabinoids, impact human health.
What’s more, scientists have discovered that we have an extensive network of endocannabinoid receptors in our bodies. This has been termed the endocannabinoid system (ECS). This system makes our bodies very receptive to the potential health benefits of cannabinoids.
As a functional medicine physician as well as a medical doctor, I’m always interested in learning more about natural ways to take back our health. I’d like to share with you what I’ve discovered about the endocannabinoid system and CBD. With knowledge, you can make the best decisions about the tools you can use on your journey to optimal health.
What is Cannabis?
The complexity of the cannabis or Cannabis sativa plant is due to its distinct compounds. There are more than 500 of them! These include terpenoids, flavonoids, omega fatty acids, and over 100 different cannabinoids. Cannabinoids are found only in the cannabis plant.
The most well-known cannabinoid is THC or delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol. This is responsible for the psychoactive effects of being “high.” It alters mental capacity and motor function.
Before we go any farther, let me explain the two types of cannabis plants: hemp and marijuana. Hemp has been used for more than 10,000 years as a source of fiber, protein, and oils. Industrial hemp has been used to make items including paper, clothing, rope, and building materials. It has far less THC (below 0.3%) than marijuana and simply cannot get anyone “high.”
The purpose of THC in the cannabis plant is for survival. Cannabis grows in many different environments. From tropical regions to cold mountainous regions, cannabis has successfully adapted due to the protective cannabinoid, THC, in the plants. It prevents herbivores from eating the plant, protects the plant in cold weather, minimizes water loss, and attracts pollinators.1
However, the story doesn’t end here. There is also a cannabinoid called CBD or cannabidiol. This does not cause a high, and possesses medically useful properties.
What is CBD?
Right now, CBD is the most promising cannabinoid. Because the hemp plant is legal throughout the United States and doesn’t have enough THC to cause a “high,” it is a good source of CBD.
According to the World Health Association, “In humans, CBD exhibits no effects indicative of any abuse or dependence potential….To date, there is no evidence of public health related problems associated with the use of pure CBD.”
Furthermore, CBD has been effective in treating some of the cruelest childhood epilepsy syndromes, such as Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. These typically don’t respond to antiseizure medications. CBD was able to reduce the number of seizures, and in some cases, stop them altogether. After controlled clinical trials, the FDA recently approved the first cannabis-derived medicine for these conditions, Epidiolex, which contains CBD.2
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
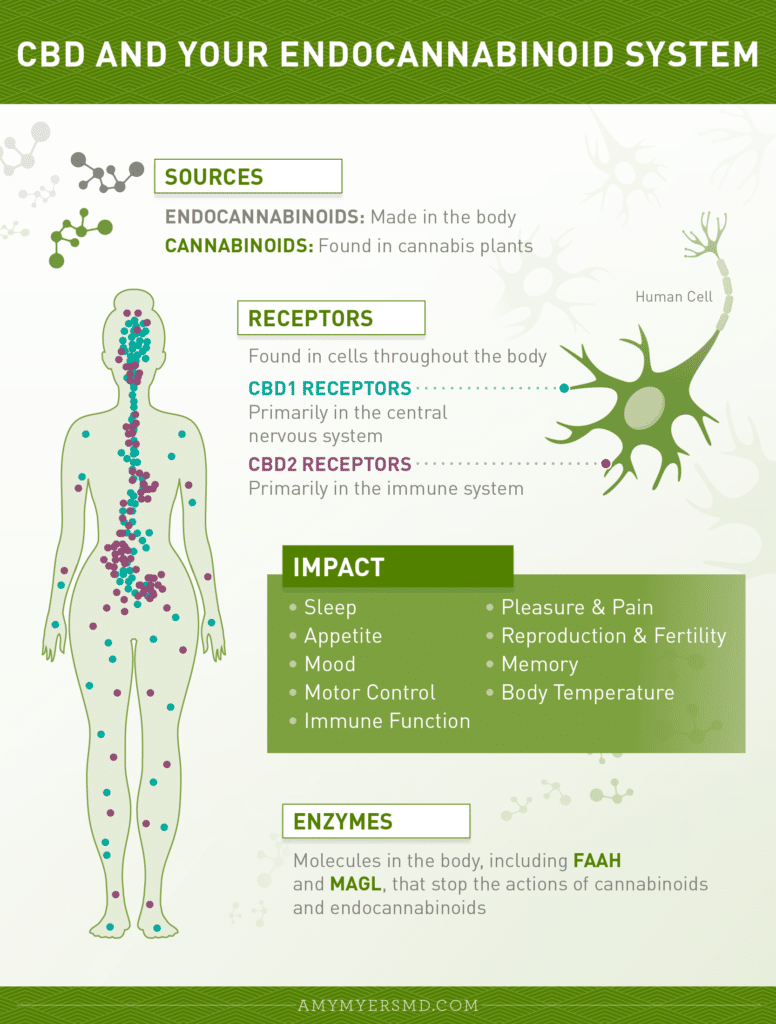
An astonishing fact is that our bodies actually produce chemicals similar to ones in the cannabis plant, called endocannabinoids. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a unique communications system that is very extensive and elaborate.
It consists of three main components: endocannabinoids, cannabinoid receptors, and the enzymes that break the cannabinoids down. The ECS exists throughout our bodies. For example, it’s on immune cells in our bloodstream, all over our nervous system, on the entire axis of the spinal cord, and in virtually every cell in the brain. There are even cannabinoid receptors in our skin.
The role of the endocannabinoid system is to keep our bodies in a state of complete balance called homeostasis. When we achieve internal homeostasis, we experience peak health. The ECS system regulates pain, stress, appetite, energy, cardiovascular function, reward perception, reproduction, and sleep, to name a few.
A lack of homeostasis can be caused by an endocannabinoid deficiency. More research is needed to determine standards and establish a clinical endocannabinoid deficiency or CECD. However, a deficiency has been linked to IBS, migraines, and fibromyalgia. In the meantime, let’s take a closer look at the main components of the endocannabinoid system.
 Dr. Amy Myers
February 16th, 2020
https://content.amymyersmd.com/article/cbd-and-your-endocannabinoid-system/CBD And The Three Parts of Your Endocannabinoid System – Infographic – Amy Myers MD®
Dr. Amy Myers
February 16th, 2020
https://content.amymyersmd.com/article/cbd-and-your-endocannabinoid-system/CBD And The Three Parts of Your Endocannabinoid System – Infographic – Amy Myers MD®Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids are naturally produced within our bodies. The two main types of these endogenous cannabinoids include anandamide (AEA) and 2-AG (or 2-arachadonoyl-glycerol).3 Anandamide was just uncovered in the 1990s! It is involved in regulating mood, memory, pain, cognition, and emotions. 2-AG is associated with pain relief, suppressing vomiting, appetite stimulation, and inhibiting tumor growth.
Cannabinoid Receptors
The second part of the ECS are the cannabinoid receptors. These are cell membrane receptors that bind cannabinoids to trigger cell responses. There are cannabinoid receptors in the brain as well as nearly everywhere else in the body.4 There are two main types.
CB1 receptors are mainly in the central nervous system. These affect motor and cognitive function. The CB1 receptor is what responds to THC yet it also responds to the body’s naturally occurring endocannabinoids — anandamide and 2-AG.
CB2 receptors are in the immune system and play a pivotal role in neuroprotection and neuroinflammation. CBD can bind to at least 12 sites of action in the brain. These activate multiple pathways to elicit feelings of relaxation and improved mood. These action sites are also a part of the ECS.
Typically, brain cells (neurons) communicate with each other and with the rest of the body by sending chemical messages. These neurotransmitters coordinate and regulate everything we feel, think, and do.
They are released by a presynaptic cell. They then travel across a small gap (the synapse), and attach to specific receptors located on a postsynaptic cell. This spurs the receiving neuron into action, triggering a set of events that allows the message to be passed along.
However, endocannabinoid signaling works “backward.” When a postsynaptic neuron is activated, cannabinoids are made on demand from fat cells in the neuron. Then they travel backward to the presynaptic neuron, where they attach to cannabinoid receptors. Since cannabinoids act on presynaptic cells, they can control what happens when these cells are activated.
Enzymes
The third part of the system is the enzymes that break down the endocannabinoids. The enzyme FAAH works quickly on the chemicals our bodies produce, like anandamide, but not on external cannabinoids. This is why THC produces a high and anandamide doesn’t.
What Are the Benefits of CBD?
Now we know that your body makes its own cannabinoids called endocannabinoids. We also have an understanding of the endocannabinoid system. Next let’s look at the main benefits of CBD, which activates your ECS.
Some key benefits of CBD are its ability to make improvements in:
- Anxiety and insomnia – CBD changes the way your brain responds to serotonin, which is the “feel good hormone” and promotes sleep.
How are CBD Products Made?
CBD products are made when the CBD compound is extracted from the cannabis sativa plant — either hemp or marajuana — and blended with a carrier oil or food product. There are topical creams and salves, sublingual CBD which is dropped under the tongue for quicker absorption, and oils. There are also other delivery systems including suppositories and forms of CBD that can be vaped or inhaled. There are even CBD edibles and gummies.
Among the most common forms of CBD is oil to be taken orally. To make it, the CBD compound is mixed with a carrier oil such as coconut, hemp seed, or medium-chain triglyceride (MTC) oil, sometimes with added flavorings. You can drop the oil directly in your mouth or under your tongue, hold for a minute or two, and then swallow. It can also be incorporated into beverages.
CBD oil benefits include its easy absorption by the body as well as it’s relatively low cost compared to other forms. There are a few types of CBD oil: full-spectrum CBD oil, broad-spectrum CBD oil, and CBD isolate.
Full-Spectrum CBD Oil
Full-spectrum CBD oil is made from a process which isolates the cannabinoids from the hemp plant. It includes all the types of cannabinoids, including cannabinol (CBN), cannabigerol (CBG), and as well as THC. However, since the full-spectrum CBD is made from hemp, the levels of THC are less than .3% and thus cannot result in a “high.”
Broad-Spectrum CBD Oil
The process to make broad-spectrum CBD oil removes even trace amounts of THC yet leaves all the other cannabinoids.
CBD Isolate
CBD Isolate is another option for consumers. This form of CBD comes in the form of a crystalline solid or white powder. This most refined form is 99% pure CBD with no other cannabinoids or other compounds.
Is CBD Legal?
Both the hemp-derived and marijuana-sourced CBD have legal constraints that depend upon where in the US you live. Effective January 2019, the 2018 Farm Bill legalized the production of hemp plants with THC content below 0.3%, placing hemp-derived CBD products under the guidance of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Thus, hemp-derived CBD products (with less than 0.3 percent THC) are legal on the federal level, but are still illegal under some state laws. Marijuana-derived CBD products are illegal on the federal level, but are legal under some state laws. Check your state’s laws and those of anywhere you travel.
Is CBD Right for You?
Because CBD is still so new and the rules governing it are confusing, manufacturing and marketing CBD products are currently a “Wild West” environment. Thus, it’s important to source products from companies you trust to ensure you are purchasing a product contains nothing more or less than the ingredients you think it does. Aim for products created from organically-grown plants which are non-GMO and pesticide-free.
CBD oil for anxiety is one of the most common uses. It may be used for anxiety disorders, or for short-term anxiety associated with specific events, such as public speaking. Discuss the options, including the appropriate dose of CBD, with your doctor if you suspect it could help you on your journey to your best health. Be aware of possible side effects including:
- Irritability. This has been most often seen with the Rx version for epilepsy, which is a high dose.
- Interactions. CBD can increase effects of the blood thinner coumadin as well as certain other medications.
Remember there is still much research underway regarding CBD, so if you do choose to try it, I advise starting with a smaller dose and working your way up if necessary. Stop using CBD products altogether if you have negative side effects.
CBD research has shown tremendous promise in helping those with serious conditions such as MS and epilepsy. It can also be a support in chronic pain management for those suffering from arthritis and many other painful conditions.
As I have mentioned in the past, new research can take many years to filter into clinical practice in conventional medicine. As a functional medicine professional, my goal is to help you on your journey to your best health. Take control of your health by staying informed of new research and findings to see if CBD may be right for you.
Article Sources
- https://www.leafly.com/news/science-tech/why-does-cannabis-produce-thc.
- https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-drug-comprised-active-ingredient-derived-marijuana-treat-rare-severe-forms.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22801993.
- https://weedmaps.com/learn/cannabis-and-your-body/endocannabinoid-system/.
